Quantum Entanglement: Spooky Action at a Distance - The Weirdest Phenomenon in Physics?

Quantum Entanglement: Spooky Action at a Distance - The Weirdest Phenomenon in Physics?
Einstein famously called it "spooky action at a distance." Quantum entanglement is arguably one of the strangest and most counterintuitive phenomena in all of physics. But what exactly is it, and why does it hold such fascination for scientists and science enthusiasts alike? Let's dive into the mind-bending world of quantum mechanics to explore this perplexing concept.
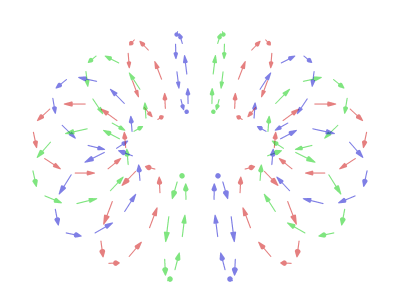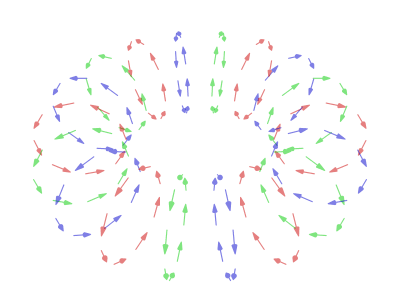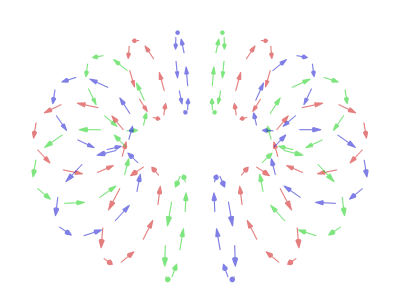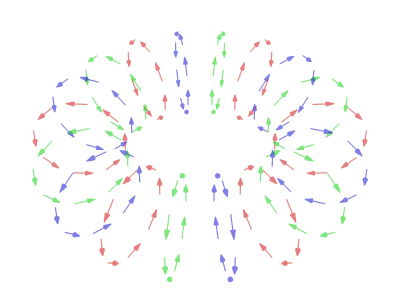
At its core, quantum entanglement describes a situation where two or more particles become linked in such a way that they share the same fate, no matter how far apart they are. This means that if you measure a property of one particle, you instantly know the corresponding property of the other particle, even if they are light-years away. This instantaneous connection baffled even Einstein, who couldn't reconcile it with his theory of relativity, which states that nothing can travel faster than light.

EntanglementDistillationSketch by Qcomp, licensed under Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
To understand entanglement, it's helpful to first grasp a few basic principles of quantum mechanics. One key concept is superposition, which states that a quantum particle can exist in multiple states simultaneously until measured. For example, an electron's spin can be both "up" and "down" at the same time. When we measure the spin, the superposition collapses, and the electron "chooses" one state or the other. Now, imagine two entangled electrons. Their spins are correlated. If you measure one electron and find its spin is "up," you instantly know the other electron's spin is "down," even without measuring it. This correlation exists regardless of the distance separating the electrons.
The implications of quantum entanglement are profound. It challenges our classical understanding of space and time, suggesting that these concepts may not be as fundamental as we once thought. While entanglement doesn't allow for faster-than-light communication (as the outcome of the measurement on one particle is random), it has potential applications in various fields, including quantum computing and quantum cryptography. Quantum computers could leverage entanglement to perform computations that are impossible for classical computers. Quantum cryptography could use entanglement to create unbreakable encryption keys, ensuring secure communication.
Source: Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
Despite its potential, quantum entanglement is still a subject of ongoing research and debate. Scientists are working to better understand the fundamental principles underlying this phenomenon and to explore its full range of applications. Experimental verification of entanglement has been achieved in numerous labs around the world, solidifying its place as a real and measurable aspect of the quantum world.
As physicist Asher Peres wrote, "Unperformed experiments have no results." This quote highlights the crucial role of measurement in defining reality at the quantum level. The act of observing or measuring a quantum system fundamentally alters its state. In the context of quantum entanglement, this implies that the correlation between entangled particles is only revealed through measurement.
Key Takeaways
Reliable Sources
Suggested search query: "quantum entanglement experimental verification"
Share this mind-bending concept with your friends and spark a quantum conversation!
Further Reading
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0