A Star That Vanished Without a Trace: The Mystery of the Failed Supernova
Explore the enigmatic phenomenon of stars that vanish without a trace. Learn about failed supernovae and how massive stars collapse directly into black holes without a brilliant explosion.

A star that vanishes without a trace. One such mysterious case is that of a massive star that appears to quietly collapse into a black hole without the dramatic supernova explosion we expect.

NASA/ESA/C. Kochanek (OSU), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Mystery of a Vanishing Star
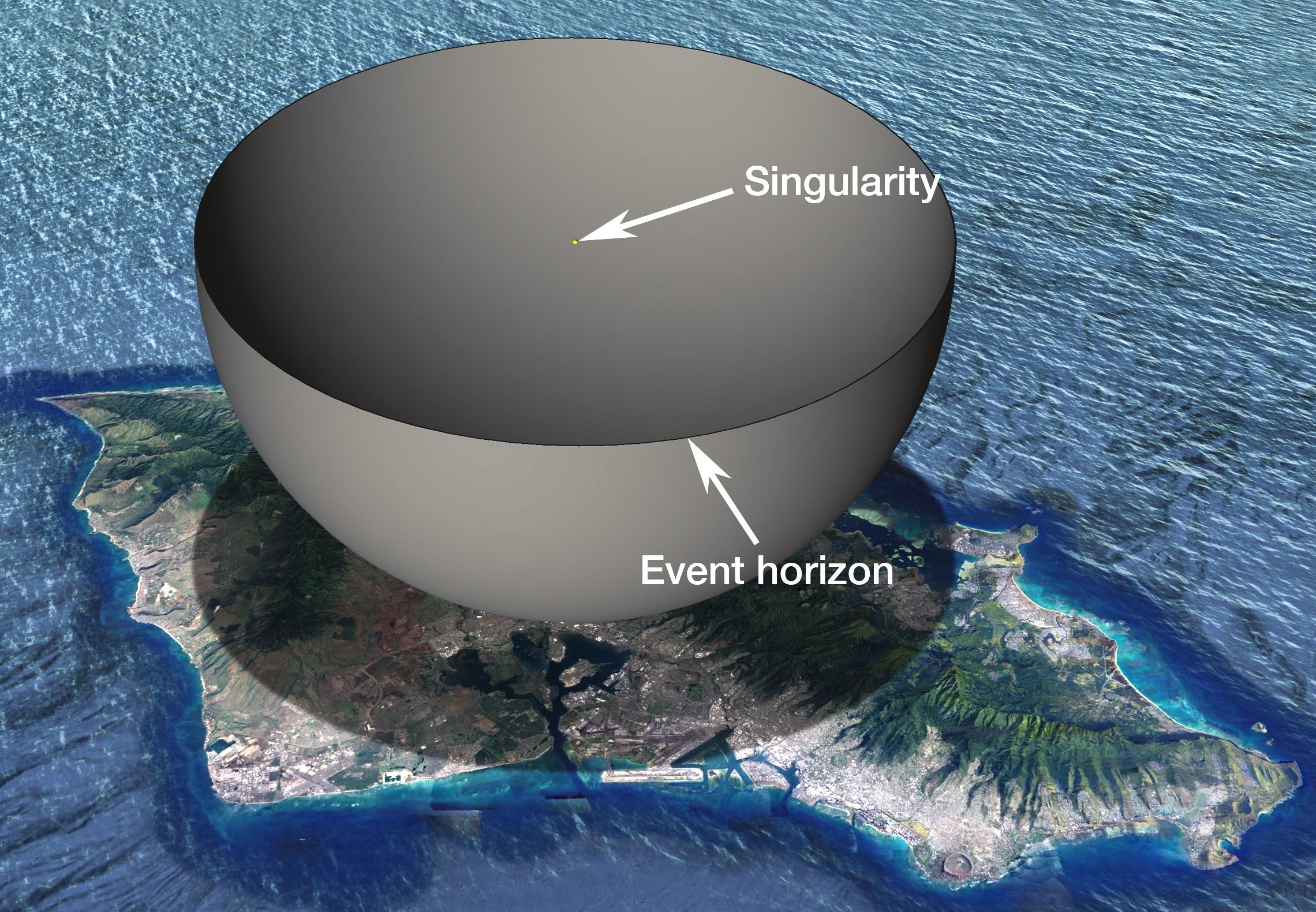
Imagine watching a bright star suddenly fade away into darkness with no warning flash or lingering debris. This is not a scene from science fiction – it is a real astrophysical puzzle. Observations of certain massive stars have revealed cases where a star's light diminishes and it ultimately disappears from optical view. This phenomenon suggests that instead of a conventional supernova, some stars may undergo a “failed supernova” – a direct collapse into a black hole.
Scientific Explanations: Failed Supernovae and Direct Collapse
Under normal circumstances, a dying massive star explodes as a supernova, scattering its enriched elements across the cosmos. However, when a star is extremely massive, its core’s collapse might not trigger a powerful explosion. Instead, the core contracts so rapidly that the star collapses directly into a black hole with little to no explosive signature.
Several theories have been proposed to explain these vanishing stars:
- Failed Supernova: The star's core collapses and forms a black hole while most of the star’s outer layers are swallowed or ejected with minimal luminosity.
- Direct Collapse: In some cases, the gravitational forces are so strong that the star simply “disappears” from view without a bright transient event.
- Neutrino Emission: Energy is lost predominantly through neutrinos, particles that interact so weakly with matter that their release leaves behind almost no observable light.
Observational Evidence: What Astronomers Have Found
One of the best-studied examples is the star known as N6946-BH1, located in galaxy NGC 6946. Initially observed as a luminous red supergiant, the star experienced a modest optical outburst in 2009 before gradually fading from view. By 2015, it had completely vanished in visible light – a result that supports the failed supernova scenario.
Astronomers continue to analyze archival data and employ new telescopes to search for more instances of these vanishing stars. Their findings not only refine our models of stellar evolution but also deepen our understanding of how black holes are born.
Source: National Geographic (YouTube)
In conclusion, the case of a star vanishing without a trace challenges our conventional wisdom about stellar death. The quiet collapse of a massive star into a black hole without the fanfare of a supernova explosion opens up exciting avenues of research in astrophysics, offering clues to the life cycles of the most massive stars in our universe.
Key Takeaways
Reliable Sources
Further Reading
What do you think about these mysterious stellar disappearances? Share your thoughts and join the discussion!
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0